


We are transforming aerospace by metal 3D printing lighter, efficient propulsion for satellites. Metal 3D printing enables the creation of complex thrusters and fuel tank parts with previously impossible geometries, achieving significant mass reduction and boosting satellite efficiency.
Propulsion is absolutely crucial for space satellites; without it, they wouldn’t reach their intended orbits. Once a satellite is launched, its upper stage provides the initial boost, although further adjustments are necessary to insert it into the desired orbit.
Satellite propulsion systems are miniature engines that allow satellites to manoeuvre in space, change their orbits, or even de-orbit at the end of their lifespan.
Satellites serve a multitude of purposes that impact our daily lives in numerous ways:
- Communication satellites bridge vast distances for phone calls, internet, TV and radio. These satellites need to adjust their pointing to track specific ground stations or other satellites.
- Navigation satellites like GPS (Global Positioning System) pinpoint your location on Earth.
- Earth observation satellites monitor our planet providing vital information for weather forecasting, climate and environmental monitoring. These satellites might need to manoeuvre to capture images of different areas or perform scientific measurements at specific locations.
Our proficiency in metal 3D printing has resulted in the creation of vital propulsion components for numerous satellites utilised by leading space organisations worldwide. This article delves into our specialisation in fuel thrusters and tanks. It emphasises the critical role reliable propulsion plays in ensuring a satellite’s successful mission throughout its operational life.
Metal 3D Printing Lighter, Efficient Thrust Chambers
Satellites rely on various propulsion systems, often smaller thrusters. These thrusters play a key role in altitude control, ensuring the satellite keeps its antennas, instruments, and solar panels pointed in the correct direction.
The materials used in 3D printing for satellite propulsion must be able to withstand the harsh environment of space, including extreme temperatures, radiation and vacuum. That is why Inconel 718 and to a lesser extent, Titanium, are the materials of choice.
These thrusters are designed to use liquid propellant. They often use a combination of nitrous oxide and propylene and the reason is:
- Higher performance: liquid propellants pack more punch (energy release) for thrust, allowing for sharper moves and quicker satellite response.
- Scalability – adjustable liquid flow lets these thrusters fit a wider range of satellites.
Many of the thrust chambers we 3D print have complex internal channels for fuel/oxidiser mixing. Capable of operating in two distinct modes – hot gas and cold gas – satellite thrusters provide a versatile spectrum of control. Hot gas thrusters deliver the raw power necessary for significant manoeuvres, while cold gas thrusters offer the precise touch needed for delicate adjustments.
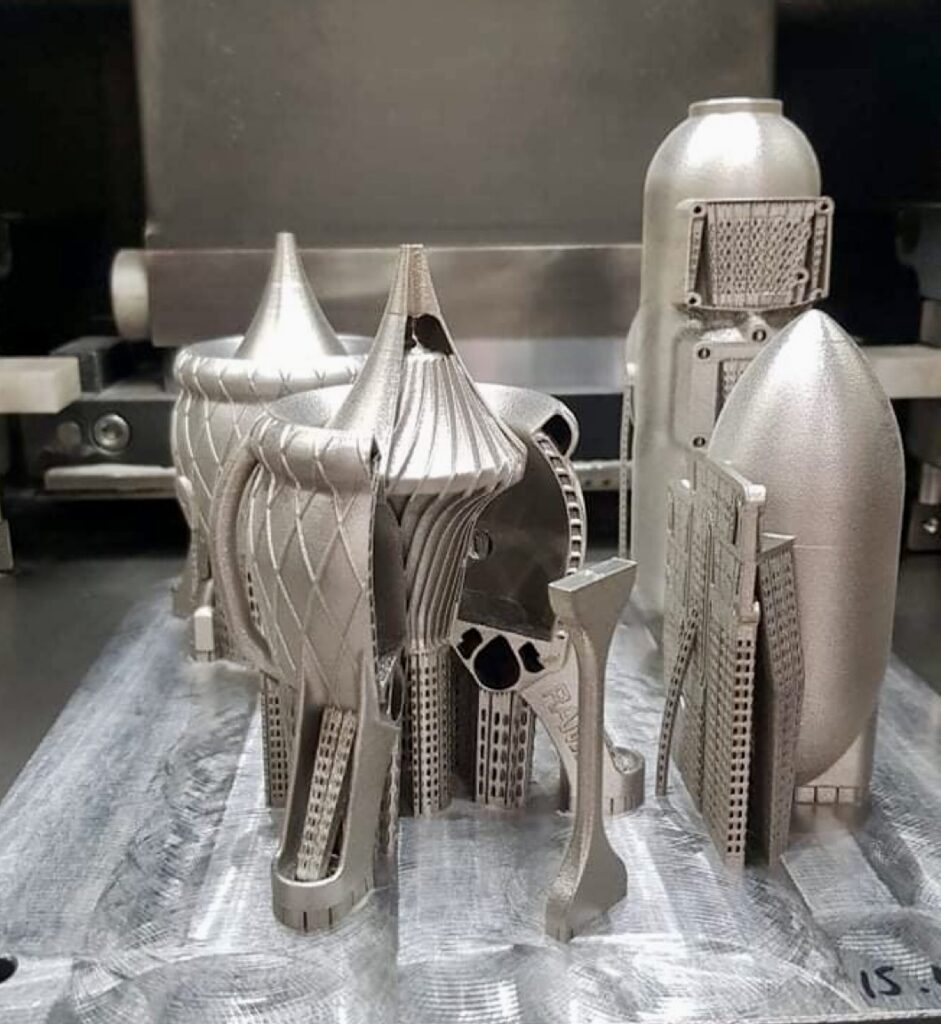
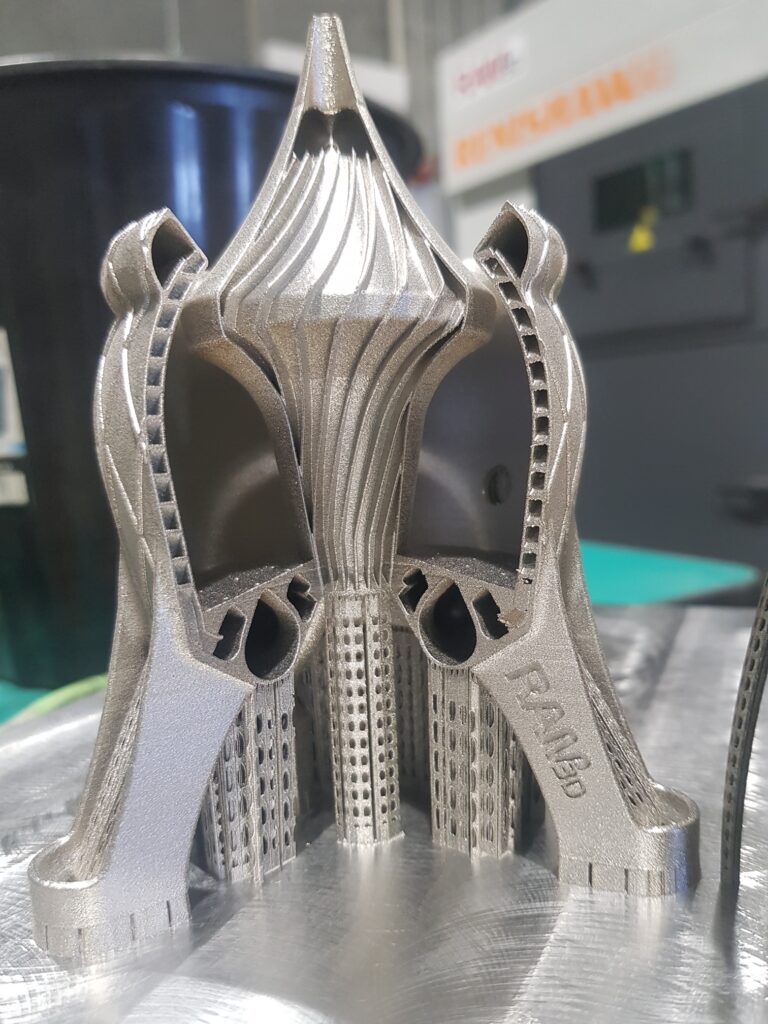

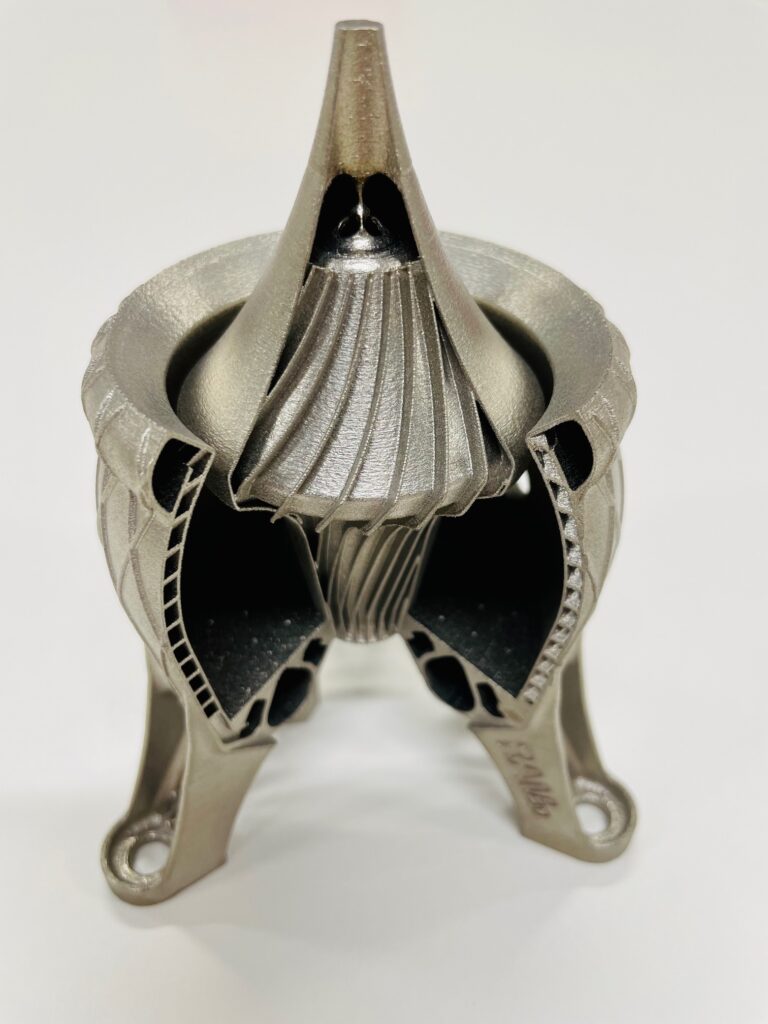
3D Printed Fuel Tanks
There are many different types of fuel tanks, and we will concentrate on the one we print most frequently. The fuel tank in satellite propulsion serves a critical purpose, providing steady and complete propellant flow, even in the challenging microgravity environment. This translates to better thruster performance, improved fuel efficiency, and ultimately, a more successful mission for the satellite.
Fuel tanks are either single or dual. Dual fuel tanks, featuring a smaller tank nestled within a larger one, integrate all essential piping for streamlined fuel management. Our extensive aerospace 3D printing experience ensures these tanks meet design pressures, having successfully produced numerous units.
Most commonly we print these tanks in Inconel 718 due to its resistance to a large range of chemicals, however, we have printed a few in titanium 64 depending on the fuel used.
Over a decade of collaboration with our spacecraft partners has proven 3D printing’s potential to revolutionise satellite production. By eliminating expensive tooling and minimizing material waste, metal 3D printing significantly reduces costs. 3D printing also allows for rapid prototyping and iteration, which can help to shorten satellite development cycles.
We understand the complexity of spacecraft, with over 8,000+ components incorporated into spacecraft and rockets. Our clients are confident of our qualification and certification process that the 3D components we print for them meet the same strict qualification and certification requirements as traditionally manufactured parts. Our meticulous quality control systems actively verify consistent, high-quality parts.
